NAD+ and Immunity
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, abbreviated as NAD+, is a vital component of all living cells in our body. It is synthesized in our body from vitamin B3 (Niacin or nicotinamide ). It is converted into various forms in the body, like:
- Oxidized form or NAD+
- Reduced form or NADH.
- Phosphorylated form NADP+ or NADPH
It acts as a coenzyme in many important metabolic reactions and is a key metabolic regulator of our body. It also plays a major role in the generation of energy in the form of ATP.
The level of NAD+ decrease in the body with age. and a decreased level of NAD+ is linked with many chronic diseases and cancer.
The increasing level of NAD+ improves the deficit caused by NAD+ deficiency and improves cognition, restores muscle mass, boosts the immune system, and controls longevity. Nicotinamide supplements are very effective at raising blood levels of NAD+.
It has many important health benefits like increase lifespan, improves performance of the Mitochondria under physiological stress, protecting against metabolic complications, and boost the immune system.
The immune system protects our body from invaders like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and cancers. It consists of the following components:
- An innate immune system that is inherited and is present since birth. It acts as a first responder and is consists of different cells like macrophages and phagocytes.
- B-Cells recognize the invaders and produce antibodies that destroy the pathogens.
- T-Cells mature in the thymus and are a very important component of our immune system. They can differentiate into different types of cells.
- Cytotoxic T Cells (CD-8) that attack infected cells and induce their death by a process called Apoptosis.
- Memory Cells are derived from cytotoxic cells and persist in the body even after the infection has resolved. They serve as a memory of that infection and hang around to fight any recurrence.
- Helper T Cells (especially Th1, Th17) secret chemicals called cytokines that control the function of the B cells and activate cytotoxic cells.
NAD+ and related compounds are very important for the proper functioning of our immune system. Several studies have demonstrated that NAD+ is essential for the activation of the immune system and its differentiation into specialized cells, and prolong survival of immune cells. It also provides the energy required for the proper working of the immune system.
A study has demonstrated that nicotinamide decreases susceptibility to Staphylococcus Aureus infection and it can be used in its treatment as well as prevention. [1]
Another research has shown that NAD+ supplementation improves age-related immunosuppression, protects against viruses, and enhances vaccine response. [2]
Let's discuss each of these in detail.
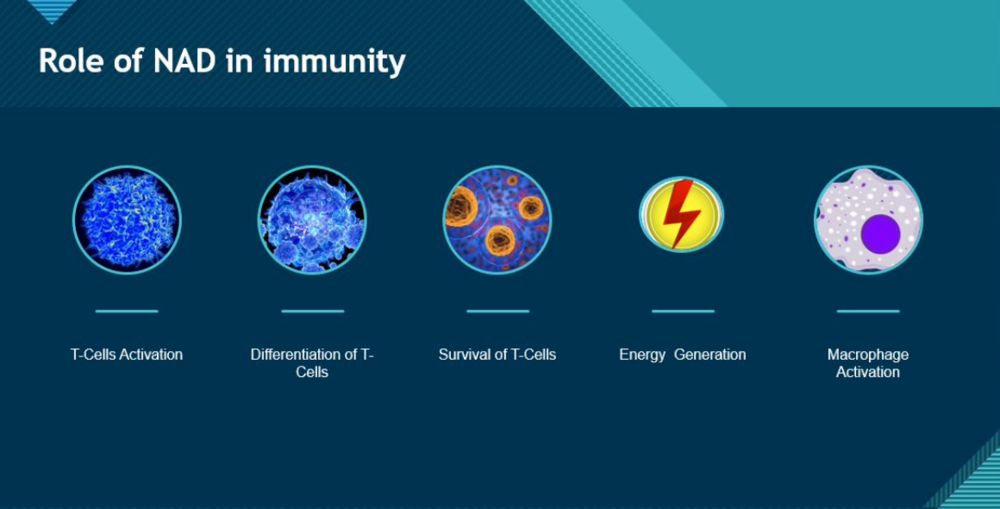
T cells are a very important component of our immune system that regulate our immune response, kill infected cells, produce cytokines, and activate other components of the immune system.
A high level of NAD+ is essential for the activation of the T-cells. This action is mediated by increased intracellular calcium concentration and the release of certain cytokines.
In cancer, NAD+ is depleted in the body, and the ability of the body to fight infections is compromised. This can be restored with NAD+ supplementation.
This has also been demonstrated that NAD+ supplementation boost T cells, increase killing of tumor cells, and enhance survival of the organism. NAD+ supplementation also increases the efficacy of the anti-cancer drugs. [4]
T Cells are produced in the bone marrow and then go to the thymus for differentiation into fully functional cells. This differentiation is critical to get different types of T-cells that can fight all kinds of pathogens.
NAD+ concentration has a well-documented role in the differentiation of naïve T-cells into specialized cells. [5]
Sirtuin is a protein that is also involved in the differentiation of memory T cells. A high level of NAD+ is required to activate Sirt-2 and in turn to achieve a powerful immune system. On the other hand, NAD+ is depleted in some tumors and that leads to immune suppression. [6]
Another mechanism by which NAD+ affects the differentiation of T-cells is through Mast cells. Mast cells mediate the differentiation of CD+ T cells both in the presence of antigen-presenting cells (APC) and without APC. This NAD+-mediated differentiation made the mice resistant to Listeria infection that would have been lethal otherwise. [7]
NAD+ controls the survival of immune cells and induces apoptosis in immature Cells. While activated or memory cells are resistant to NAD+-induced cell death. [8]
NAD+ results in metabolic reprogramming of T cells that enable them to stay longer in the host with superior tumor control.
This has been further confirmed by the studies that utilized drugs to inhibit NAD+ and it resulted in decreased functioning of T helper cells. [9]
Energy is also required in the form of ATP for the proper functioning of immune cells especially during a period of infection or stress. NADH acts as an electron donor during the process of ATP synthesis via the electron transport chain.[10]
Macrophages are very important component of the immune system that detects, engulf, and destroys bacteria and other harmful pathogens. They also release various cytokines that activate other immune cells.
NAD+ level controls the activation of macrophages and control of infections. For example, NAD+ supplementation saved rats from a very high dose of bacterial products (LPS) that caused death in other Rats. [11]
Interferon Gamma (IFN-γ) is secreted by activated Macrophage and serve many important functions like:
- Increase macrophage activation
- Increase recognition of pathogens by the immune cells
- Attract immune cells at the site of infection
- Facilitate anti-bacterial and anti-viral immunity
Nicotinamide treatment results in increased secretion of IFN-γ and hence increases immune response. [12]
COVID-19 was first identified in the Wuhan city of China and it rapidly became a matter of global concern. A lot of options are being used with variable success.
NAD+ supplementation protects the body against COVID-19 infection at several stages:
- As NAD+ is an important component of innate immunity so it acts as a first-line defense against the entry of COVID-19 and other viruses into the body. This defense mechanism consumes NAD+, so if NAD+ sources are not repleted these immune defenses may be compromised. [13]
- When viruses are entered into the body and start replicating, Sirtuins are the enzymes that control the replication of the virus. Sirtuins are also NAD+-dependent enzymes, and won't work if the level of NAD+ is decreased in the body.[14]
- When an attack of the virus occurs, another enzyme called PARP gets activated. PARP is essential for the activation of the Macrophages that destroy viruses. This enzyme also utilizes NAD+, and deficiency of NAD+ will result in increased survival of the Virus.[14]
- COVID-19 activates an enzyme called ADAM17 that results in the release of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL-6). Sirtuin (NAD+-dependent) downregulates the ADAM17 and other inflammatory compounds and prevents this hyperinflammatory response.
The deficiency of NAD+ increases the susceptibility of the individuals to the COVID-19 infection. [15]
A phase-II study has found out that a combination of nutritional supplements including NAD+ resulted in a significant decrease in recovery time. [16]
A trial of NAD+ supplementation to treat severe COVID-19 in the elderly is also being done and is showing promising results. [3]
According to FDA, oral supplementation of NAD+ is safe and well-tolerated in animal studies and human trials. Many studies have demonstrated the efficacy of NAD+ supplementation but no side effect has been reported in the literature. [17]
NAD+ plays a very important role in boosting our immunity against infections and cancer. The level of NAD+ decreases with age and it is necessary to restore its level to remain protected from pathogens. NAD+ supplementations are a safe and effective way of boosting immunity.
Kyme, P., Thoennissen, N. H., Tseng, C. W., Thoennissen, G. B., Wolf, A. J., Shimada, K., Krug, U. O., Lee, K., Müller-Tidow, C., Berdel, W. E., Hardy, W. D., Gombart, A. F., Koeffler, H. P., & Liu, G. Y. (2012). C/EBPε mediates nicotinamide-enhanced clearance of Staphylococcus aureus in mice. The Journal of clinical investigation, 122(9), 3316–3329. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI62070
Minhas, P.S., Liu, L., Moon, P.K. et al. Macrophage de novo NAD+ synthesis specifies immune function in aging and inflammation. Nat Immunol 20, 50–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0255-3
Effects of Nicotinamide Riboside on the Clinical Outcome of Covid-19 in the Elderly (NR-COVID19) status: recruiting, available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04407390
Yuetong Wang, Fei Wang, Lihua Wang et al. Potentiating the anti-tumor response of tumor infiltrated T cells by NAD+ supplementation doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.21.001123
Navarro, M. N., Gómez de Las Heras, M. M., & Mittelbrunn, M. (2021). Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolism in the immune response, autoimmunity and inflammageing. British journal of pharmacology, 10.1111/bph.15477. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15477
Jiang, C., Liu, J., Guo, M., Gao, X., Wu, X., Bai, N., Guo, W., Li, N., Yi, F., Cheng, R., Xu, H., Zhou, T., Jiang, B., Sun, T., Wei, S., & Cao, L. (2020). The NAD-dependent deacetylase SIRT2 regulates T cell differentiation involved in tumor immune response. International journal of biological sciences, 16(15), 3075–3084. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.49735
Rodriguez Cetina Biefer, H., Heinbokel, T., Uehara, H., Camacho, V., Minami, K., Nian, Y., Koduru, S., El Fatimy, R., Ghiran, I., Trachtenberg, A. J., de la Fuente, M. A., Azuma, H., Akbari, O., Tullius, S. G., Vasudevan, A., & Elkhal, A. (2018). Mast cells regulate CD4+ T-cell differentiation in the absence of antigen presentation. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology, 142(6), 1894–1908.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.01.038
Liu, Z. X., Azhipa, O., Okamoto, S., Govindarajan, S., & Dennert, G. (2001). Extracellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide induces t cell apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 167(9), 4942–4947. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.167.9.4942
Morandi, F., Horenstein, A. L., & Malavasi, F. (2021). The Key Role of NAD+ in Anti-Tumor Immune Response: An Update. Frontiers in immunology, 12, 658263. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.658263
Xie, N., Zhang, L., Gao, W., Huang, C., Huber, P. E., Zhou, X., Li, C., Shen, G., & Zou, B. (2020). NAD+ metabolism: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 5(1), 227. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00311-7
Cameron, A. M., Castoldi, A., Sanin, D. E., Flachsmann, L. J., Field, C. S., Puleston, D. J., Kyle, R. L., Patterson, A. E., Hässler, F., Buescher, J. M., Kelly, B., Pearce, E. L., & Pearce, E. J. (2019). Inflammatory macrophage dependence on NAD+ salvage is a consequence of reactive oxygen species-mediated DNA damage. Nature immunology, 20(4), 420–432. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-019-0336-y
Scatozza, F., Moschella, F., D'Arcangelo, D., Rossi, S., Tabolacci, C., Giampietri, C., Proietti, E., Facchiano, F., & Facchiano, A. (2020). Nicotinamide inhibits melanoma in vitro and in vivo. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR, 39(1), 211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01719-3
Budayeva, H. G., Rowland, E. A., & Cristea, I. M. (2015). Intricate Roles of Mammalian Sirtuins in Defense against Viral Pathogens. Journal of virology, 90(1), 5–8. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.03220-14
Katrina Bogan-Brown, Yasmeen Nkrumah-Elie, Yusrah Ishtiaq, Philip Redpath & Andrew Shao (2021) Potential Efficacy of Nutrient Supplements for Treatment or Prevention of COVID-19, Journal of Dietary Supplements, DOI: 10.1080/19390211.2021.1881686
Miller, R., Wentzel, A. R., & Richards, G. A. (2020). COVID-19: NAD+ deficiency may predispose the aged, obese and type2 diabetics to mortality through its effect on SIRT1 activity. Medical hypotheses, 144, 110044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110044
Altay O, et al. 2020. Combined metabolic cofactor supplementation accelerates recovery in mild-to-moderate COVID-19. MedRxiv.
JOHN E. HUMISTONPharmacy Compounding Committee Review: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) accessed on 12-08-2021 availabel at [https://www.fda.gov/media/113016/download]


